The infection rate of Kexing three needles is only 8%? In fact, there is no significant difference in the proportion of infection with mRNA vaccine.
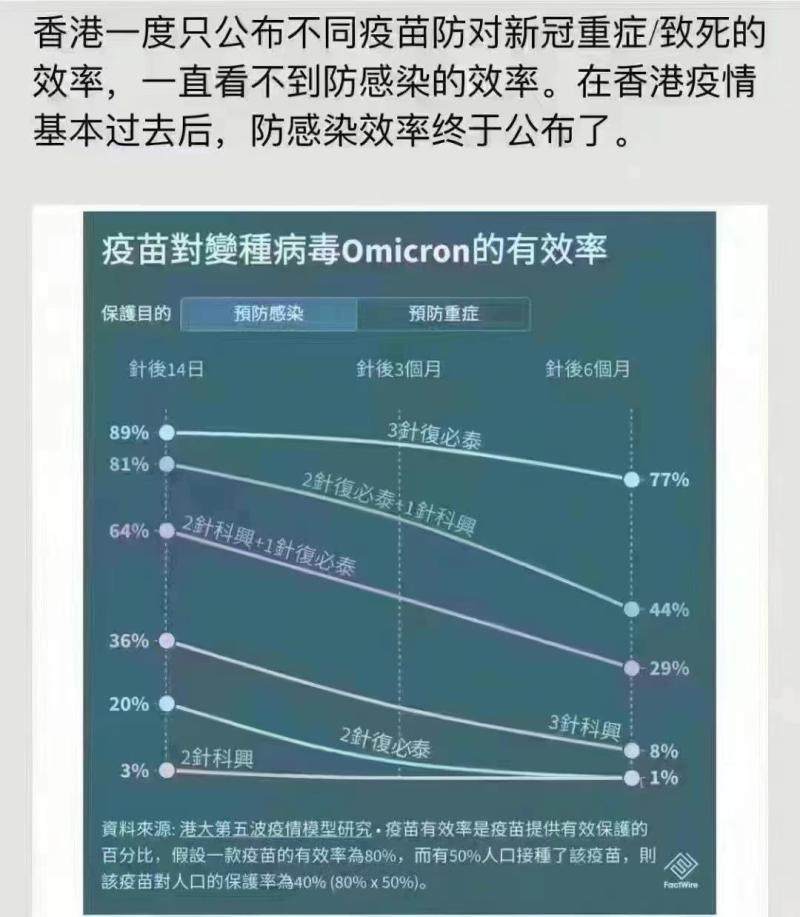
Looking at the news, recently, a data map about the infection efficiency of Kexing was circulated on the Internet, which indicated that, according to the latest data of the fifth round of epidemic in Hong Kong, the effective rate of Kexing in preventing Omicron was low. Even after the third injection, the effective rate of preventing infection was only 36% on the 14th day after inoculation, but only 8% after six months.
So, is this really the case?
This is not true statistics.
Tracing back to the source, we found that this picture was first seen in a simulation model of the epidemic development of Hong Kong universities reported by the Hong Kong investigative news agency Fax Agency in February this year. The data content is the calculated result of the model, not the real statistical data of Hong Kong society.
On February 10th, the School of Public Health of HKU released the simulation model of epidemic development in The 5th Wave [1], in which the efficiency of each vaccine combination in different periods was calculated based on the data of different medical studies. The study estimated that the effective rate of preventing Omicron variant virus infection was 36% on 14th day after the third dose of Kexing vaccine, and it dropped to 8% after 6 months.
So, what is the real situation?
According to the epidemic data released in Hong Kong on December 23rd, in the fifth round of epidemic (from December 31st, 2021 to December 21st, 2022), 2.32 million people were infected in Hong Kong, more than 7.04 million people have been vaccinated with at least one dose of vaccine, and 627,000 people have been vaccinated with the fourth dose of vaccine.
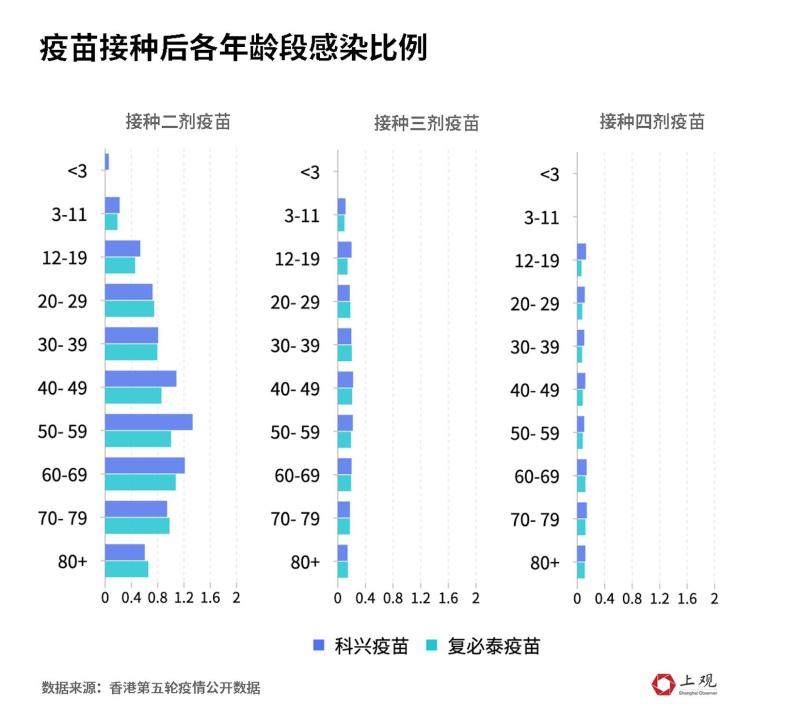
According to a rough calculation,There is no significant difference in infection ratio between inactivated vaccine and mRNA vaccine.
Taking the infection ratio after the fourth injection as an example, the average infection ratio of inactivated vaccine was 11.97%, while the infection ratio of mRNA vaccine was 8.99%, with a difference of 2.97%. This difference decreases with age. In the group over 80 years old, the proportion of infection between them is only 0.93%.
Moreover, with the increase of the number of vaccination agents, the effectiveness of preventing infection has increased.
The inactivation effect of anti-infection is slightly lower than that of mRNA vaccine.
Although there is no big difference in the actual infection rate, from the perspective of preventing infection,The effectiveness of inactivated vaccine against infection is indeed lower than that of mRNA vaccine.
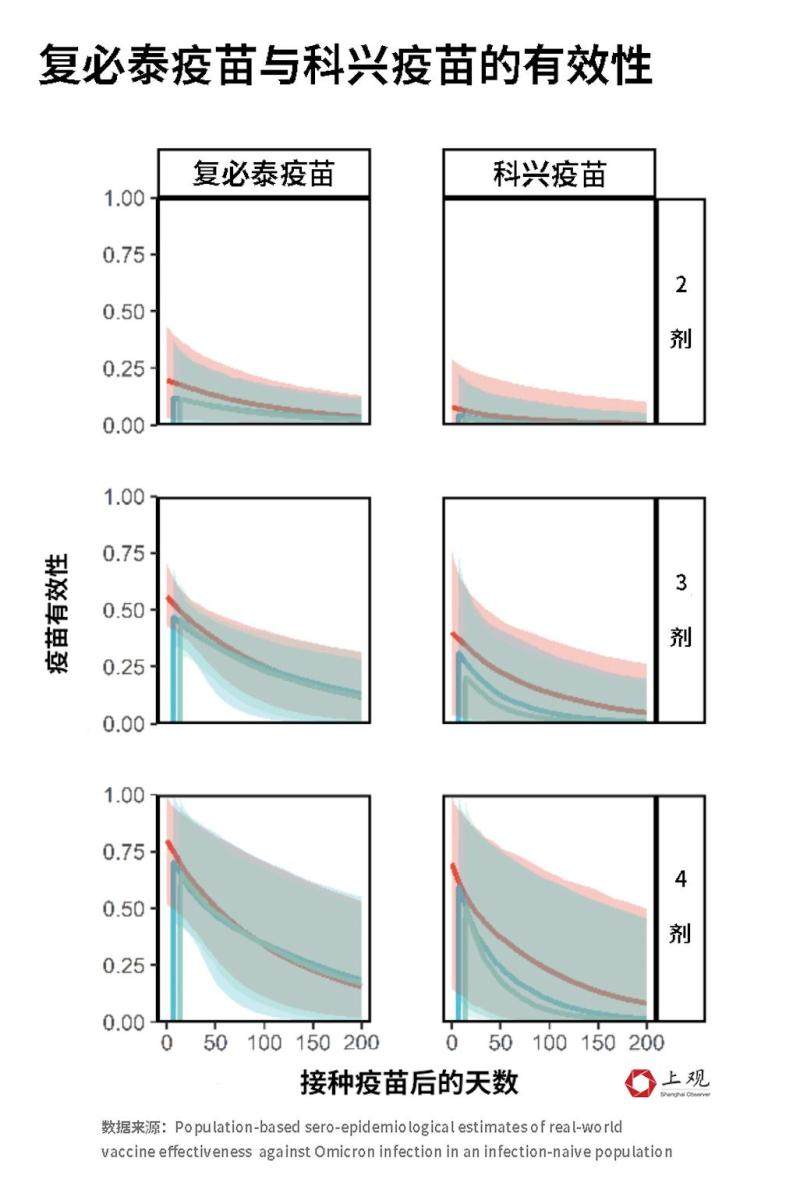
According to the paper published by the Institute of Public Health of the University of Hong Kong in November this year [2], this study analyzed the effectiveness of Fubitai and Kexing COVID-19 vaccine through the serum survey of 5310 subjects in Hong Kong.
It was found that the effectiveness of inactivated vaccine (31%) was slightly lower than that of mRNA vaccine (47%) 7 days after inoculation.
Both of them are effective in preventing COVID-19 in the short term.
But by contrast,Inactivated vaccine has a short validity period.
The effective concentration of mRNA vaccine antibody remained in blood for a long time, and the effectiveness declined by half after 104 days. The semi-decline period of inactivated vaccine is about 40 days.
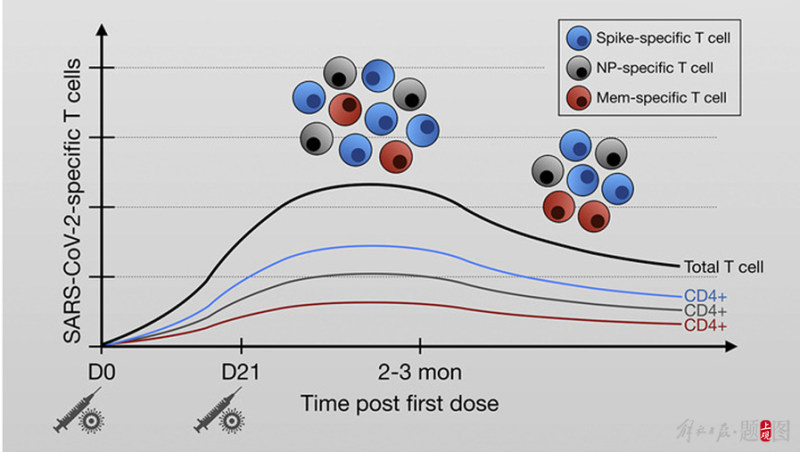
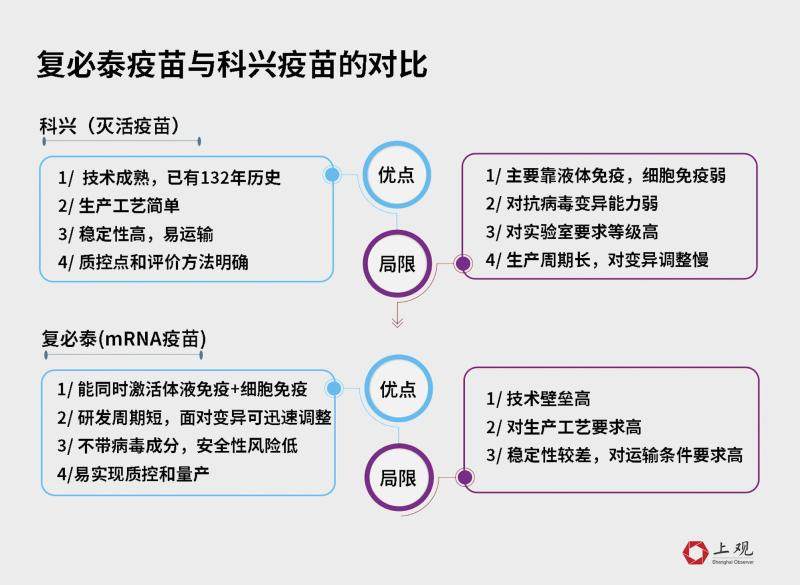
The strength of effectiveness may be related to the technology adopted by the vaccine.
The mRNA vaccine contains the messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) of the virus, and its working principle is to send instructions to the host cell to replicate the spike protein, so that the immune mechanism can produce antibodies in time to deal with the virus. The inactivated vaccine is injected with a complete, killed copy of the virus, making it impossible to replicate without causing disease.
The two technologies are different, so the effectiveness is different.
Inactivated vaccines are equally effective in preventing severe illness and death.
Although it is not effective in preventing infection, the effect of inactivated vaccine is equal to or even better than that of mRNA vaccine in preventing severe illness and death.
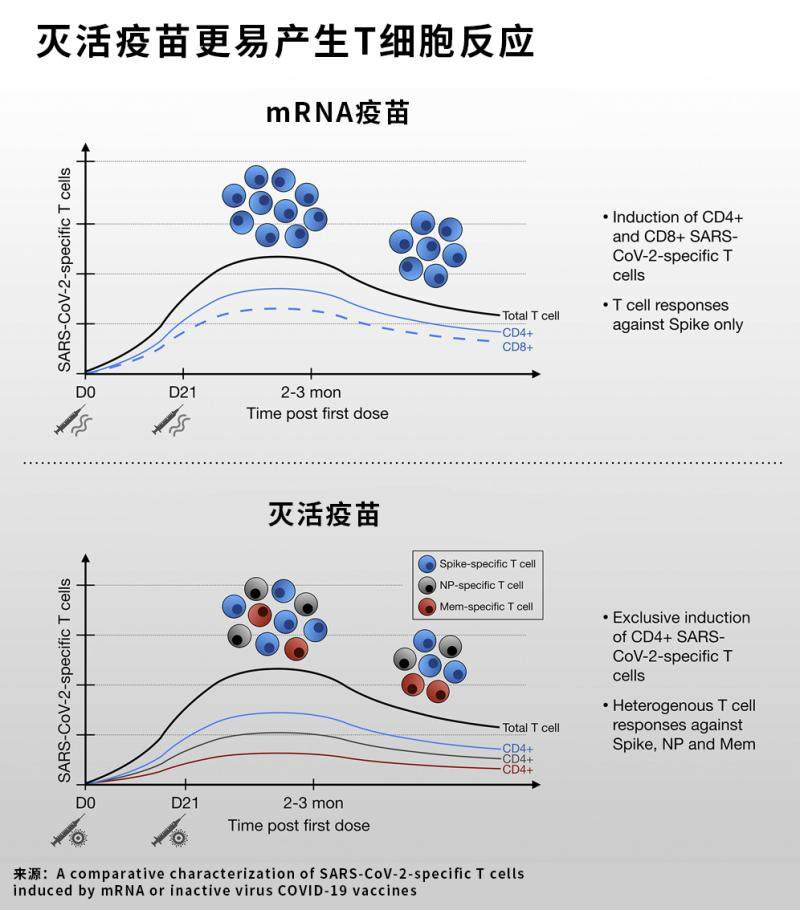
According to the paper published by the Medical College of the National University of Singapore in November this year [3], although the antibody response guided by inactivated vaccine is not as good as that of mRNA vaccine, inactivated vaccine can trigger a wide range of immune responses against different protein viruses.It is more effective against severe infection..
It is found that inactivated vaccines are more likely to produce T cell reactions against viral proteins than other types of vaccines. Inactivated vaccines stimulate cells called CD4 T, and when they recognize virus antigens, they release chemicals that become cytokines to help activate other types of immune cells.
Professor Antonio Bertoletti, who is in charge of the project, said that T cells are more effective in improving diseases than antibodies because of Omicron’s strong immune escape ability.
According to the actual data, in this round of epidemic in Hongkong, the total case fatality rate (or overall case fatality rate) is 0.71%, and the probability of the unvaccinated people dying of Covid-19 infection is 2.87%. The mortality of one dose of Kexing vaccine was 1.25%, two doses was 0.31%, and three doses was 0.04%.
In other words,The mortality rate of people without vaccination is 71.8 times higher than that of people with three doses of Kexing vaccine.
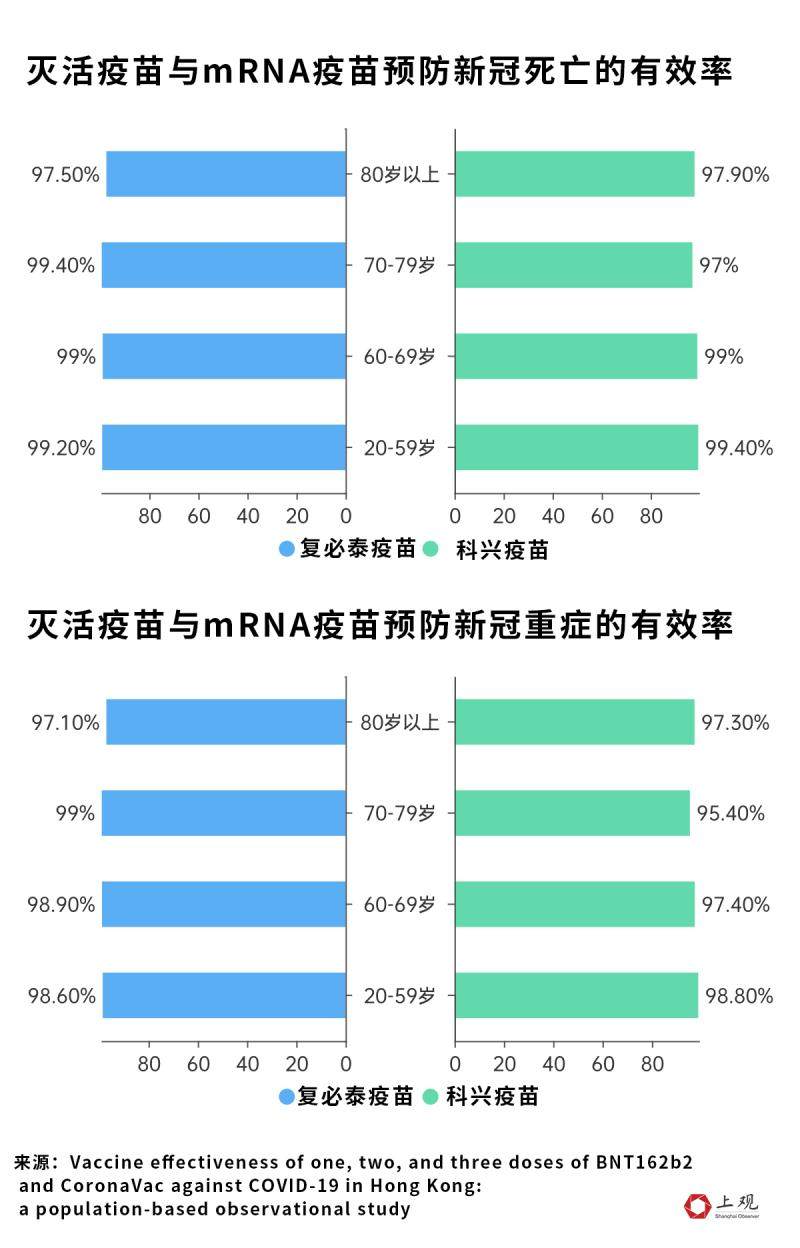
According to the paper published by the Institute of Public Health of the University of Hong Kong in July this year [4], after three injections, the effective rate of inactivated vaccine for preventing severe illness and death exceeded 95%.
On the average, inactivated vaccine is no different from mRNA vaccine. The effective rate of inactivated vaccine is 97.23%, which is only 1.18% lower than that of mRNA vaccine. In the prevention of COVID-19’s death, the effective rate of both reached 98%, and the difference was only 0.45%.
Even in some age groups, the effective rate of inactivated vaccine is better than that of mRNA vaccine. For example, for people over 80 years old, the efficiency of inactivated vaccine in preventing severe illness and death is higher than that of mRNA vaccine.
According to a paper published by the Chilean Ministry of Health in February this year [5],Inactivated vaccines are equally effective in preventing severe diseases in children and adolescents.
It was found that for children and adolescents aged 6 to 16, the effective rate of two inactivated vaccines against hospitalization was 91%, and the confidence interval was 87.8% to 93.4%. The effective rate of preventing severe illness (that is, staying in ICU) is 93.8%, and the confidence interval is 87.8% to 93.4%.
On the whole, whether it is inactivated vaccine or mRNA vaccine, booster vaccination can provide substantial protection against infection in Covid-19, including mild and asymptomatic cases.
Although Covid-19 infection in China has been adjusted to "Class B tube" at present, "keeping healthy and preventing severe diseases" is still the focus of epidemic prevention, and it is still necessary to continue to promote vaccination, especially for the elderly.
Related papers:
[1] HKU School of Medicine Briefing COVID-19 The 5th Wave epidemic development simulation model.
【2】Lau, J. J.,Cheng, S. M.,Leung, K.,Lee, C. K.,Hachim, A.,Tsang, L. C.,…& Wu, J. T. (2022). Population-based sero-epidemiological estimates of real-world vaccine effectiveness against Omicron infection in an infection-naive population, Hong Kong, January to July 2022. medRxiv.
【3】Lim, J. M. E.,Hang, S. K.,Hariharaputran, S.,Chia, A.,Tan, N.,Lee, E. S.,…& Tan, A. T. (2022). A comparative characterization of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells induced by mRNA or inactive virus COVID-19 vaccines. Cell Reports Medicine, 3(11), 100793.
【4】McMenamin, M. E.,Nealon, J.,& Lin, Y. (2022). Vaccine effectiveness of one, two, and three doses of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a population-based observational study (vol 22, pg P1435, 2022). LANCET INFECTIOUS DISEASES, 22(9), E239-E239.
【5】Jara, Alejandro, et al. "Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Children and Adolescents: A Large-Scale Observational Study."
Original title: Kexing three-needle infection prevention rate is only 8%? We found that this is not the real world data, and the truth is actually like this.
Editor: wu si
Editor: Wu Zhonglan
Audit: Feng Fei